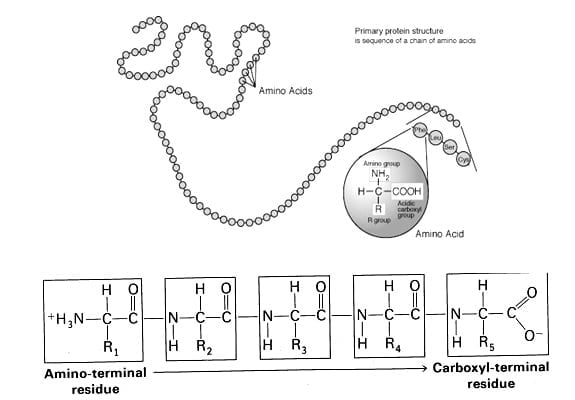
Primary Structure
The primary structure of proteins refers to the linear sequence of its amino acid structural units. Linderstrom-Lang in 1951, first coined the term “primary structure“. The primary structure sequence is determined by the nucleotide sequence of the gene which encodes the protein. The primary structure of a protein starts from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. The R groups that distinguish the various amino acids play no role in the formation of peptide backbone of proteins. A protein can consist of any sequence of amino acids. Thus, considering a protein that contains 100 amino acids could form any of 20100 different amino acid sequences. This property of proteins is extremely important because it permits great diversity.